Collaborative positioning using image sensors
| Team: | P. Trusheim, C. Heipke |
| Year: | 2019 |
| Funding: | Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) |
| Duration: | 01.12.2019 - 01.12.2022 |
Positioning is one of the main tasks in navigation. Due to the developments in autonomous driving, a constant and reliable position becomes more and more important.
This Project investigates how integer, collaborative positioning in dynamic sensor networks using GNSS and image sensors can combine the obtain sensor data to get the best possible position solution. Sensor nodes in the network are able to recognize each other and communicate their status. To determine the unknown photogrammetric point estimation via bundle adjustment is used.
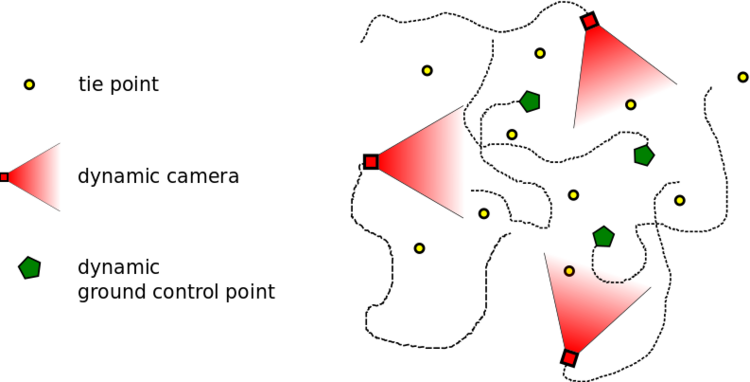
Therefore, the sensor network distinguishes three different types of nodes, illustrated in the figure above
- Dynamic cameras: These are the used image sensors; their exterior orientation is a time-depended function.
- Dynamic GCPs: These are objects with known 3D coordinates in a global coordinate system by using, for example, GNSS sensors; their 3D coordinates depended on time.
- Static tie points: The 3D coordinates of these points are not depended on time; their 3D coordinates are unknown.
Overall research project: “Integrity and Collaboration in Dynamic Sensor Networks” (i.c.sens)
This project is part of the international Research Training Group “i.c.sens” (https://www.icsens.uni-hannover.de). The aim of the Research Training Group is to investigate concepts for ensuring the integrity of collaborative systems in dynamic sensor networks.